The Applicable Federal Rate (AFR) What Works in a Changing Environment?
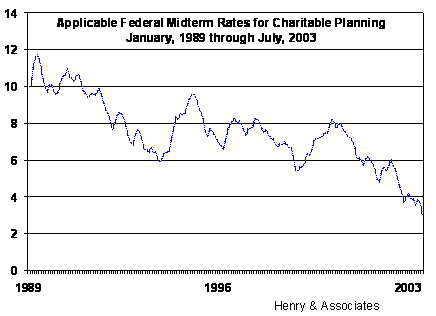
In 1988, TAMRA created a means to measure the time value of money for gift and estate planning functions. Prior to 1971, the government used 3.5% as an assumed rate, but changed to a rate that floats with debt instruments, and this rate changes monthly. Essentially, the IRS tries to determine what a stream of income or a deferred gift is worth and adjusts the value over time. For lifetime gifts, periodically updated mortality tables provide a mechanism for estimating the time portion of the time value, but whats needed in a present value/future value calculation is a way to assign a market interest rate. As a result, §7520 requires that the applicable rate be based on federal securities with maturities between three and nine years. Most estate and gift calculations use the interest rate in the month of the transfer, but for charitable gifts, there is an exception for donors who may elect to use either the current months rate or one from the previous two months. The most recent* §7520 charitable midterm rate (120%) used in charitable planning calculations is the lowest rate seen in years, and may create serious problems for donors contemplating a CRAT or CGA. Because some charitable gifts produce a remainder value for donors or heirs, and others produce an income value, the changing rates provide a seesaw effect; as the rates go up, some transfers are more attractive and others less so.
What tools and tactics work better when Section 7520 rates are down?
Private Annuities, Grantor Retained Annuity Trusts (GRAT), Charitable Lead Annuity Trusts (CLAT), and Charitable Gifts of a Remainder Interest in a farm or residence. Self Canceling Installment Notes (SCIN),Saleto an Intentionally Defective Irrevocable Trust (IDIT), and Dynasty Trusts pass more assets or reduce taxable transfers to remainder beneficiaries.
What tactics are more restricted when Section 7520 rates are depressed?
Grantor Retained Income Trusts (GRIT), Personal Residence Trusts and Qualified Personal Residence Trusts (PRT, QPRT), Charitable Remainder Annuity Trusts (CRAT may fail either the 10% remainder test or the Rev. Rul. 77-374 exhaustion test), Charitable Gift Annuities (CGA although the deduction goes down, the amount of principal attributed in the annuity payments goes up, if the annuity does not pass the 90% test, the charity offering the CGA may have a UBTI problem), Life Estates.
Which tools are generally unaffected by AFR changes?
Grantor Retained Unitrusts (GRUT), Charitable Remainder Unitrusts (CRUT), Charitable Lead Unitrusts (CLUT)
* Revenue Ruling 2003-71 indicates the July rate is 3.0%. Rates for June and May were 3.6% and 3.8%, respectively.
|
CMFR |
Jan |
Feb |
Mar |
Apr |
May |
Jun |
Jul |
Aug |
Sep |
Oct |
Nov |
Dec |
|
10.00 |
10.00 |
11.22 |
11.58 |
11.68 |
11.26 |
10.54 |
10.01 |
9.68 |
10.10 |
10.07 |
9.70 | |
|
1990 |
9.57 |
9.70 |
10.27 |
10.54 |
10.61 |
10.97 |
10.53 |
10.44 |
10.28 |
10.63 |
10.59 |
10.25 |
|
1991 |
9.78 |
9.64 |
9.41 |
9.50 |
9.62 |
9.53 |
9.66 |
9.87 |
9.59 |
9.08 |
8.69 |
8.51 |
|
1992 |
8.10 |
7.64 |
8.06 |
8.43 |
8.56 |
8.47 |
8.25 |
7.82 |
7.19 |
6.96 |
6.83 |
7.40 |
|
1993 |
7.63 |
7.50 |
7.08 |
6.56 |
6.57 |
6.41 |
6.67 |
6.40 |
6.44 |
6.02 |
5.91 |
6.10 |
|
1994 |
6.40 |
6.42 |
6.45 |
7.08 |
7.74 |
8.33 |
8.22 |
8.49 |
8.49 |
8.56 |
8.97 |
9.33 |
|
1995 |
9.54 |
9.59 |
9.34 |
8.84 |
8.58 |
8.22 |
7.56 |
7.27 |
7.68 |
7.59 |
7.35 |
7.12 |
|
1996 |
6.89 |
6.75 |
6.56 |
7.08 |
7.65 |
7.93 |
8.12 |
8.24 |
7.99 |
8.09 |
7.94 |
7.59 |
|
1997 |
7.34 |
7.68 |
7.72 |
7.82 |
8.25 |
8.19 |
8.00 |
7.69 |
7.51 |
7.63 |
7.34 |
7.25 |
|
1998 |
7.13 |
6.84 |
6.72 |
6.85 |
6.84 |
6.95 |
6.83 |
6.70 |
6.67 |
6.16 |
5.42 |
5.43 |
|
1999 |
5.59 |
5.67 |
5.80 |
6.35 |
6.28 |
6.46 |
7.01 |
7.16 |
7.19 |
7.25 |
7.32 |
7.46 |
|
2000 |
7.47 |
7.90 |
8.19 |
8.08 |
7.70 |
7.96 |
7.96 |
7.62 |
7.50 |
7.33 |
7.23 |
7.07 |
|
2001 |
6.75 |
6.10 |
6.10 |
5.95 |
5.73 |
6.04 |
6.16 |
6.01 |
5.79 |
5.52 |
4.97 |
4.78 |
|
2002 |
5.40 |
5.58 |
5.43 |
5.60 |
6.01 |
5.71 |
5.53 |
5.10 |
4.51 |
4.16 |
3.68 |
3.98 |
|
2003 |
4.12 |
3.93 |
3.89 |
3.56 |
3.82 |
3.68 |
3.06 |
|
|
|
|
|



Vaughn W. Henry
 CONTACT US FOR A FREE PRELIMINARY CASE STUDY FOR YOUR OWN CRT SCENARIO or try your own at Donor Direct Please note — there’s much more to estate and charitable planning than simply running software calculations, but it does give you a chance to see how the calculations affect some of the design considerations. This is not “do it yourself brain surgery”. When is a CRUT superior to a CRAT? Which type of CRT is best used with which assets? Although it may be counter-intuitive, sometimes a lower payout CRUT makes more sense and pays more total income to beneficiaries. Why? When to use a CLUT vs. CLAT and the traps in each lead trust. Which tools work best in which planning scenarios? Check with our office for solutions to this alphabet soup of planned giving tools.
CONTACT US FOR A FREE PRELIMINARY CASE STUDY FOR YOUR OWN CRT SCENARIO or try your own at Donor Direct Please note — there’s much more to estate and charitable planning than simply running software calculations, but it does give you a chance to see how the calculations affect some of the design considerations. This is not “do it yourself brain surgery”. When is a CRUT superior to a CRAT? Which type of CRT is best used with which assets? Although it may be counter-intuitive, sometimes a lower payout CRUT makes more sense and pays more total income to beneficiaries. Why? When to use a CLUT vs. CLAT and the traps in each lead trust. Which tools work best in which planning scenarios? Check with our office for solutions to this alphabet soup of planned giving tools.
